Zoom 修補了多個瑕疵,並回應安全與隱私問題

Facing growing security concerns, Zoom patches multiple vulnerabilities and vows to focus on top safety and privacy issues.
背景說明
As more companies shift to remote work, their use of tools to support these efforts are coming under greater scrutiny. Zoom, the video conferencing application used by over 200 million users daily, has seen a surge in popularity. However, over the last few months, the security community has reported several privacy and security issues with Zoom, culminating in a series of public disclosures that prompted a response from the Zoom CEO.
分析
Zoom-bombing
The increased remote working footprint and reliance on Zoom has led to a wave of mischief makers dropping in uninvited on insecure Zoom meetings to play offensive material, such as pornography, via Zoom’s screen-sharing feature. They’re also verbally insulting and threatening meeting participants using profane or racist language. These acts, dubbed “Zoom-bombing,” have steadily increased over the last few months.
On March 30, the FBI issued a warning after receiving multiple reports of meetings being targeted by Zoom-bombers. The agency provided its own set of mitigations to protect against Zoom-bombing, a page to report teleconference hijacking incidents and another page to report specific threats received during one of these incidents.
The recent surge in Zoom-bombing is reminiscent of CVE-2018-15715, an unauthorized command execution vulnerability discovered by Tenable researcher David Wells in November 2018. Wells detailed how this flaw could be used to hijack screen controls, spoof chat messages or kick attendees out of Zoom calls. However, the latest surge in Zoom-bombing doesn’t appear to use vulnerabilities.
In a blog post from Check Point on January 28, researcher Alexander Chailytko pointed out that unless a Zoom meeting is password-protected or the waiting room feature is enabled, the only information preventing uninvited guests from joining an existing Zoom meeting is knowing the 9- to 11-digit Zoom meeting ID. To highlight this weakness, Chailytko generated a list of potential Zoom meeting IDs and randomly selected a thousand. Four percent of the IDs worked, demonstrating a high rate of success, especially considering they were randomly chosen. Chailytko coordinated his disclosure on July 22, 2019, which resulted in changes being implemented by Zoom.
An article by ZDNet discusses how Zoom-bombers are getting increasingly organized, congregating across multiple online platforms including Discord, Reddit and Twitter to coordinate mass Zoom-bombings and share meeting IDs collected via social media and internet-scraping scripts. Zoom-bombers are not just coming together to randomly invade meetings, but also offering it as a service for people to submit their business or educational meeting codes to intentionally disrupt meetings and online lectures.
The collection of potentially unprotected Zoom meeting IDs and related credentials is trivial for people with basic coding and web-scraping skills. On April 2, investigative journalist Brian Krebs tweeted about a tool that makes the process even easier.
Automated Zoom conference meeting finder 'zWarDial' discovers ~100 meetings per hour that aren't protected by passwords. The tool also has prompted Zoom to investigate whether its password-by-default approach might be malfunctioning https://t.co/dXNq6KUYb3 pic.twitter.com/h0vB1Cp9Tb
— briankrebs (@briankrebs) April 2, 2020
The zWarDial tool, created by Trent Lo and other members of SecKC, attempts to bypass measures Zoom has put in place to prevent automated meeting scans by routing its scans through multiple proxies in Tor. The article in Krebs’ tweet notes that a single instance of zWarDial “can find approximately 100 meetings per hour” with a 14-percent success rate. The potential meetings discovered per hour also increases with each subsequent deployment of the tool. SecKC shared a chart showing the roughly 2,400 open Zoom meetings they discovered over a 24-hour period, indexed by industry.
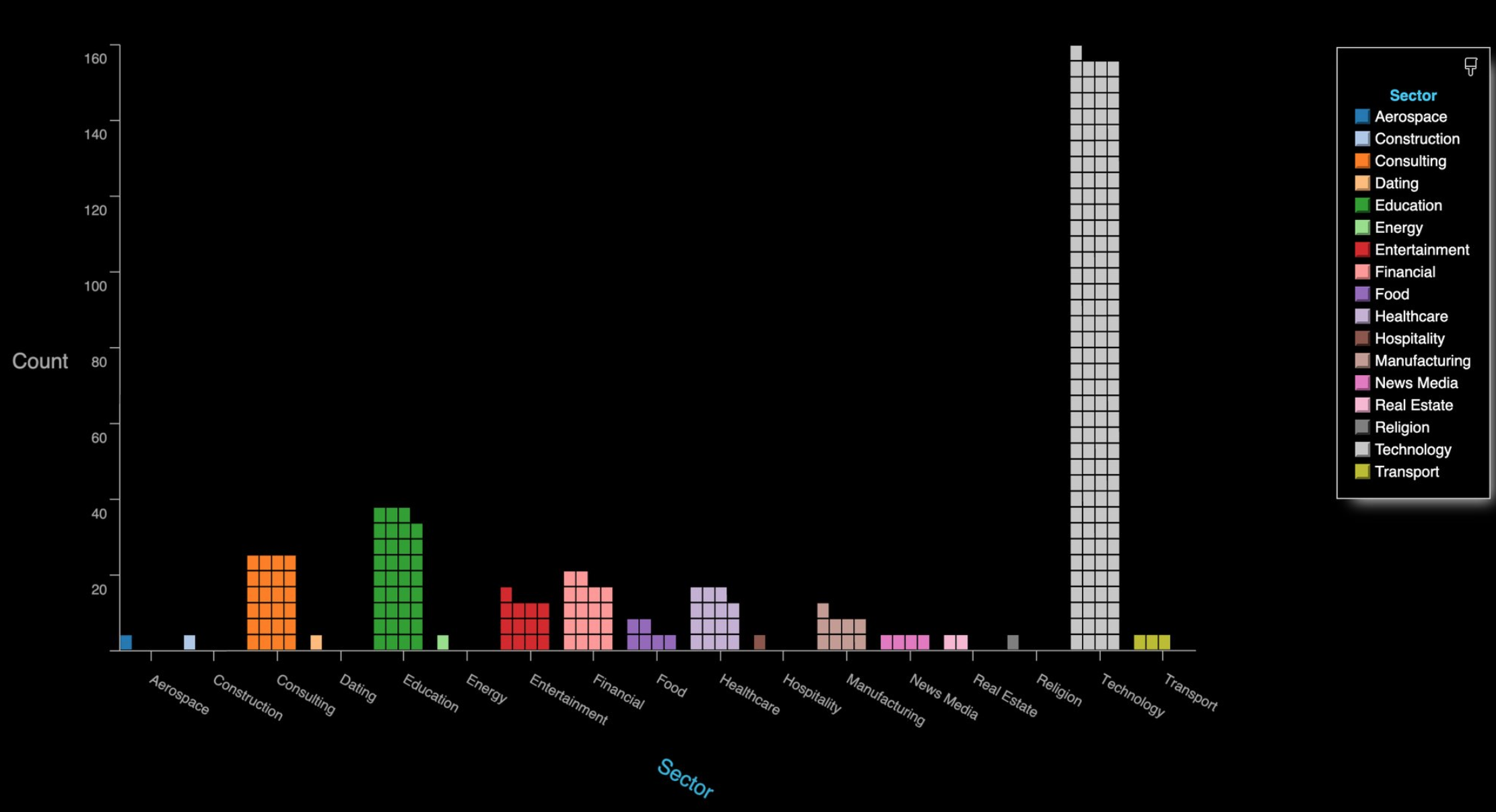
Zoom originally responded to the threat of Zoom-bombing in a blog post on March 20, offering tips on how to configure Zoom’s privacy settings to keep uninvited guests out of meetings.
Zoom Windows client: UNC path injection
On April 1, Zoom announced a fix for a flaw in the Windows client. Previously, the handling of universal naming convention (UNC) links in Zoom chat rooms could have exposed Net-NTLM-v2 hashes to an attacker, who could then utilize tools like hashcat to crack these hashes.
Security researcher _g0dmode first identified the issue on March 23.
#Zoom chat allows you to post links such as \\x.x.x.x\xyz to attempt to capture Net-NTLM hashes if clicked by other users.
— Mitch (@_g0dmode) March 23, 2020
In a tweet, _g0dmode noted that the Zoom client “allows you to post links such as \\x.x.x.x\xyz to attempt to capture Net-NTLM hashes.”
The following week, security researcher Hacker Fantastic demonstrated the UNC path injection in a tweet.
Hi @zoom_us & @NCSC - here is an example of exploiting the Zoom Windows client using UNC path injection to expose credentials for use in SMBRelay attacks. The screen shot below shows an example UNC path link and the credentials being exposed (redacted). pic.twitter.com/gjWXas7TMO
— Hacker Fantastic (@hackerfantastic) March 31, 2020
To take advantage of the flaw, an attacker would need to be in a Zoom session and convince attendees to click a specially crafted link. When a user clicks the link containing the UNC path, Windows attempts to connect to the remote site using the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol. As a default, Windows sends the user’s login name and NTLM password hash, which could potentially be cracked and used by a malicious actor. The successful exploitation of this flaw can be mitigated by following Microsoft’s guidance on restricting outgoing NTLM traffic to remote servers, or by updating Zoom to version 4.6.9 or later.
Zoom macOS installer and client: Local privilege escalation and code injection
In the macOS installer and client, multiple vulnerabilities were identified and disclosed.
The first vulnerability stems from the way Zoom installer utilizes pre-installation scripts to unpack the application. An attacker with local access could abuse these pre-installation scripts to elevate privileges to root by monitoring for the presence of the Zoom installer or updater and modifying one of the scripts during this process.
The second vulnerability is a code injection flaw in Zoom that results from its use of the “disable library validation” entitlement, which allows applications that use Hardened Runtime to load unsigned frameworks, plugins or libraries. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability to access the user’s camera and microphone via this entitlement. This could be achieved by renaming the ‘libssl.1.0.0.dylib’ file under the Zoom frameworks, creating a malicious version that acts as a proxy which references the original library file along with malicious code.
Privacy concerns
Over the past several weeks, Zoom has received scrutiny from the security community concerning the data collection and privacy implications of using the application. On March 26, VICE published a report that revealed Zoom’s iOS application was sending analytics data to Facebook even when Zoom users didn’t have a Facebook account. Zoom confirmed it had implemented the “Login with Facebook” feature using the Facebook software development kit (SDK), which collects device data. In response to the news, Zoom removed the Facebook SDK from its iOS application, promising to review its “process and protocols for implementing these features in the future to ensure this does not happen again.”
The New York Times article published on April 2 highlights another instance of data mining in which Zoom usernames and email addresses were matched to LinkedIn accounts. This feature was implemented using the LinkedIn Sales Navigator, which covertly sent a person’s username and email address to Zoom’s internal systems each time they enter a meeting. Other attendees who subscribed to the LinkedIn service could view information associated with meeting participants, including job titles, employer names and locations, even if the attendees chose not to use their real names. The removal of LinkedIn Sales Navigator was included in Zoom’s public memo on April 1 as part of its renewed focus on privacy issues.
Zoom also faced increased scrutiny around whether or not its service had implemented end-to-end encryption. In a response from Zoom on April 1, the company clarified that encryption is used to “protect content in as many scenarios as possible, and in that spirit, we used the term end-to-end encryption.” Zoom notes that to keep data encrypted in the transmission process, it uses several specialized clients including:
- Zoom Telephony Connector
- Zoom Conference Room Connector
- Skype for Business Connector
- Cloud Recording Connector
- Live Streaming Connector
In a blog post on March 29, Zoom responded to privacy and security concerns, indicating that while the company is not changing its practices, it had updated its privacy policy to be “more clear, explicit, and transparent”
概念驗證
While no proof-of-concepts (PoCs) exist for the flaws, the blog post detailing the Zoom vulnerabilities in the macOS installer and client contains enough information to develop PoCs.
Vendor response
Zoom CEO Eric Yuan published a blog post on April 1, addressing several of the privacy and security issues that had been raised. He said that over the next 90 days, the company will be doing a feature freeze, shifting their focus toward addressing “trust, safety, and privacy issues.” This includes enhancements to Zoom’s bug bounty program, the creation of a CISO council, penetration testing and weekly webinars to update the community.
解決方法
When creating Zoom meeting rooms, do not make them public. When configuring a meeting, opt for Zoom to create a randomly generated ID, rather than checking the personal meeting ID option. Set meetings to private and be sure to require a password.
Also, disable the join before host option to prevent potential trouble before hosts arrive at the meeting, assign a co-host to help moderate the meeting and enable the Waiting Room to view attendees before the meeting commences.
Additional precautions include disabling allow removed participants to rejoin and file transfer.
On April 2, Zoom released version 4.6.9 of its Windows and macOS clients to address several of the flaws reported over the last few weeks.
找出受影響的系統
A list of Tenable plugins to identify these vulnerabilities will appear here as they’re released.
取得更多資訊
加入 Tenable Community 的 Tenable 安全回應團隊。
深入瞭解 Tenable,這是用於全面管理新型攻擊破綻的首創 Cyber Exposure 平台。
索取 Tenable.io Vulnerability Management 的 30 天免費試用。
- Remote Workforce
- Vulnerability Management

