Cybersecurity Snapshot: Log4j Anniversary, CI/CD Risks, Infostealers, Email Attacks, OT Security

Get the latest on the anniversary of the Log4j crisis; OWASP’s top CI/CD risks; a surge of infostealer malware; the fund transfer fraud — business email compromise connection; and more!
Dive into six things that are top of mind for the week ending Dec. 9.
1 - One year after Log4j crisis, what have we learned?
It was at around this time last year that the discovery of the zero-day Log4Shell vulnerability in the ubiquitous Log4j open source component sent shockwaves through the worlds of IT and cybersecurity.
One year later, we’ve learned from recently released Tenable telemetry research that Log4j’s Log4Shell remains very much an issue. Tenable found that, as of October 1, 2022:
- 72% of organizations remain vulnerable to Log4Shell.
- 29% of vulnerable assets saw the reintroduction of Log4Shell after full remediation was achieved.
- Nearly one third of North American organizations have fully remediated Log4j (28%), followed by Europe, Middle East and Africa (27%), Asia-Pacific (25%) and Latin America (21%).
How long will this Log4Shell problem linger? Back in July, the U.S. Cyber Safety Review Board published a 50-plus page report on the Log4j event, and a key takeaway was that Log4Shell is an “endemic vulnerability” that’ll be around for a decade — or perhaps longer.
Given this reality, and the almost inevitable eruption of another crisis of Log4j’s magnitude, we asked Tenable CIO Patricia Grant and CSO Robert Huber for their insights and advice to help IT and cybersecurity leaders deal with vulnerabilities and threats that call for “all hands on deck” responses.

Their recommendations include:
- Foster and maintain constant and open collaboration and communication between the CIO, CSO and all other stakeholders involved in protecting the organization from cyberthreats.
- Ensure you have a full, continuously updated and actively managed IT asset inventory.
- Draft a detailed rapid-response response playbook for dealing with high-impact vulnerabilities.
To get all the details, read the blog “Are You Ready for the Next Log4Shell? Tenable’s CSO and CIO Offer Their Advice”.
And swing by Tenable’s Log4j resources page, which has links to FAQs, white papers, blogs, plugins, how-to videos, on-demand webinars and more.
For more coverage of the Log4j crisis’ anniversary and of Tenable’s Log4Shell remediation data, read these articles on Dark Reading, IT Brew, ZDNet, TechTarget, Security Week, Inside Cybersecurity, BetaNews and ISSSource.
2 - OWASP’s top 10 CI/CD security risks
With a bright spotlight shining on the security of the software supply chain, the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) recently announced a new project: the “Top 10 CI/CD Security Risks” framework.

It’s a hot topic for DevSecOps teams tasked with developing and delivering application updates quickly yet securely, so that the code they release has fewer vulnerabilities, misconfigurations and other flaws.
With the “Top 10 CI/CD Security Risks” framework project, OWASP seeks to help DevSecOps teams fine-tune their security strategies by not only identifying and defining each challenge, but also explaining their impact and offering recommendations.
Here’s the list of OWASP’s top risks for CI/CD (continuous integration / continuous delivery) ecosystems:
- Insufficient Flow Control Mechanisms
- Inadequate Identity and Access Management
- Dependency Chain Abuse
- Poisoned Pipeline Execution (PPE)
- Insufficient PBAC (Pipeline-Based Access Controls)
- Insufficient Credential Hygiene
- Insecure System Configuration
- Ungoverned Usage of 3rd Party Services
- Improper Artifact Integrity Validation
- Insufficient Logging and Visibility
For more information about this project, read a blog post about it and visit the project page and its GitHub page.
3 - Attackers boost use of infostealer malware
The popularity of information stealer (infostealer) malware is growing, thanks to this malware type’s effectiveness at harvesting victims’ data, along with its low cost, ease of use and broad availability via malware-as-a-service (MaaS) providers.
That’s according to the Accenture Cyber Threat Intelligence (ACTI) team, which has detected a jump in demand for infostealer malware on the dark web, as well as an increase in the volume of victim data logs available for purchase in credential marketplaces.
“ACTI expects the infostealer landscape to continue to evolve and pose a significant risk to organizations in 2023,” reads an Accenture blog about the findings.
For example, the number of logs available in the highly popular Russian Market grew by almost 40% to 4.5 million between July and October.
Another finding: in response to the surge in interest in infostealer malware, new variants are being peddled in underground marketplaces.
Infostealers Malware Advertisements and Pricing from July to October 2022
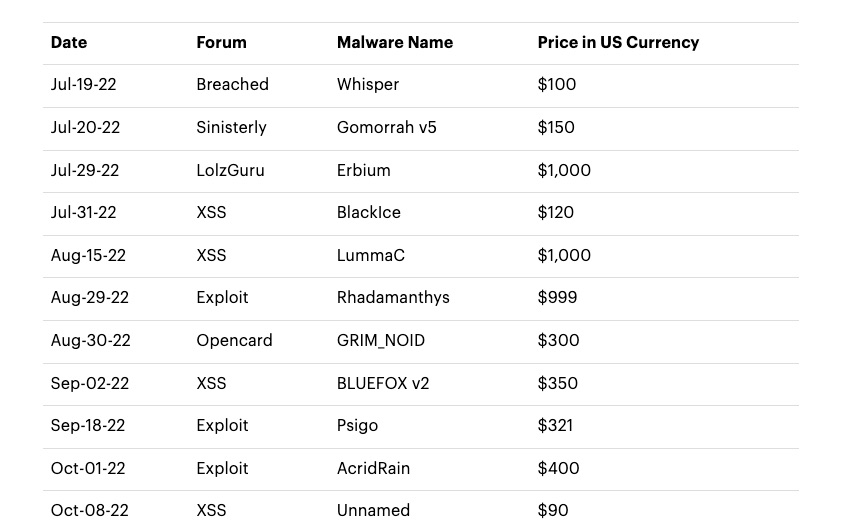
(Source: Accenture Cyber Threat Intelligence team, December 2022)
As cybercriminals successfully swipe credentials using infostealer malware, they will often launch “MFA-fatigue” attacks to breach compromised accounts that are protected with multifactor authentication.
In MFA fatigue attacks, hackers, armed with stolen usernames and passwords, bombard victims with mobile push notifications to annoy them until they approve the request, unaware that they’re granting a cybercriminal access to their account.
Recommendations from Accenture include:
- Shift from MFA methods that rely on users approving push notifications to ones where users enter randomly generated codes or authenticate using biometrics.
- Double down on security awareness efforts, training employees on topics like MFA fatigue attacks and social engineering tactics.
- Stay on top of the latest developments in infostealer malware, including new tactics, techniques and procedures.
For more information:
- “Implementing Phishing-resistent MFA” (U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency -- CISA)
- “Multi-Factor Authentication Request Generation” (MITRE)
- “Infostealer Malware Market Booms, as MFA Fatigue Sets In” (Dark Reading)
- “New Infostealer Malware 'Erbium' Offered as MaaS” (Security Week)
- “MFA fatigue attacks are on the rise: How to defend against them” (CSO)
"Hacking Two Factor Authentication: Four Methods for Bypassing 2FA and MFA" (The CISO Perspective)
"Not all MFAs are created equal" (CISA)
4 - Cybersecurity looms large in SMB software purchases
Heightened concerns among small and medium size businesses (SMBs) in the U.S. have made cybersecurity a key factor in their software purchasing decisions.
That’s according to a new report from software marketplace Capterra that found cybersecurity is top of mind as 75% of the 500 SMBs surveyed said they plan to boost their software spending in 2023.
How is cybersecurity influencing these plans?
- Among their motivations for purchasing software, respondents ranked concerns about cybersecurity in third place (32%) for the first time behind the perennial top two: the need to improve productivity (38%) and to keep up with growing IT needs (34%).
- The “IT architecture and security software” category topped all others in 2022 SMB purchases.
- When evaluating any type of software, SMBs’ top criteria for deciding whether or not to purchase a product was its security (42%), beating out factors like features (39%).
Drivers for SMB software purchases
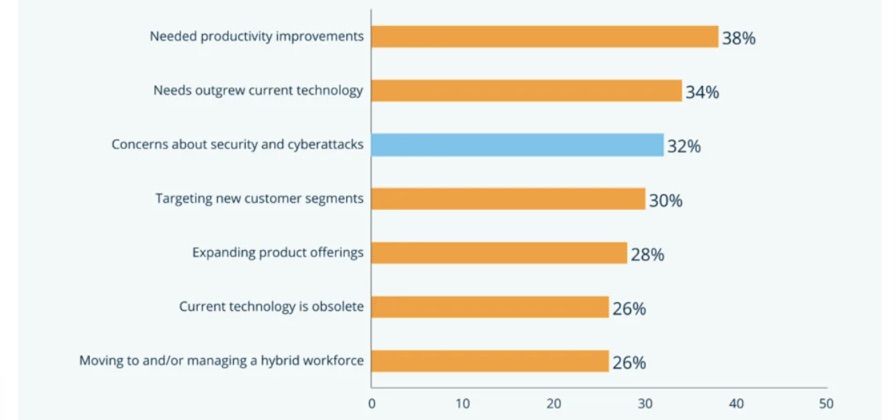
(Source: Capterra’s “2023 U.S. SMB Software Buying Report,” November 2022)
The report’s recommendations for evaluating the security of a software product include:
- Don’t take vendors’ words at face value. Do your due diligence and ask vendors specific questions about security features, such as multifactor authentication and data encryption.
- Find out vendors’ processes for disclosing, patching and updating vulnerabilities in their software products.
For more information, read Capterra’s “2023 U.S. SMB Software Buying Report.”
To learn more about assessing the security of a software product:
- “How to Assess a Vendor's Data Security” (Electronic Frontier Foundation)
- “5 Key Questions When Evaluating Software Supply Chain Security” (Dark Reading)
- “CISA issues supply chain security guide for software buyers” (Tenable)
- “Software Supply Chain Security Guidance” (U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology)
- “6 Ways to Optimize Vendor Management Programs” (IANS Research)
"What is patch management?" (TechTarget)
5 - Don’t sleep on funds transfer fraud
Fraudulent funds transfer (FFT) doesn’t get the attention it warrants despite being among the most prevalent, disruptive and costly types of cyberattacks, according to insurance company Corvus.
In its latest Risk Insights Index report, Corvus found that FFT — a social engineering attack in which employees are duped into transferring money to cyber criminals — accounts for the largest slice of its claims pie since 2019 at almost 28%.
Corvus Cyber Claims Since 2019
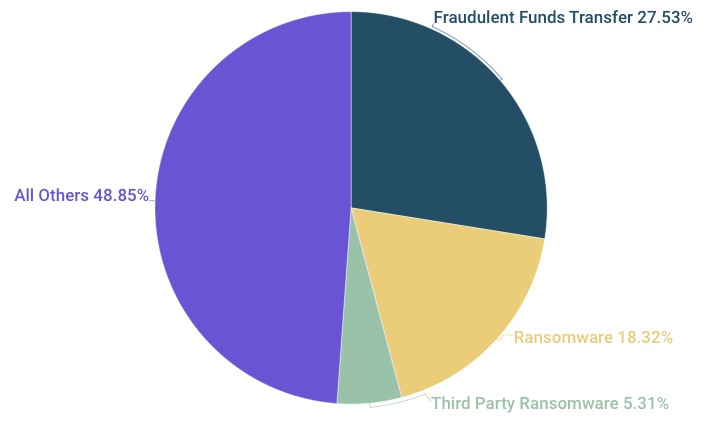
(Source: “Corvus Risk Insights Index Q4,” Corvus, December 2022)
And FFT’s incidence is trending higher. It’s never fallen below 25% of all Corvus claims in the past six quarters, and reached an all-time high (36%) in Q3 2022. “FFT is a prominent, but still under-discussed element of overall cyber risk,” reads the report, whose sources include Corvus’ IT security scanning technology and claims data.
So what’s the main takeaway for security teams? Dial up your efforts at preventing business email compromise (BEC), which is by far the most common technique used in FFT incidents — 70% according to Corvus claims data. Often, BEC attacks will not only result in FFT but also in takeover of email accounts, which opens up a broader attack path for the hackers.
For more information about FFT and BEC:
- “How can we help you? Business Email Compromise” (U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation)
- “Business Email Compromise” (Techopedia)
- “Security Primer – Business Email Compromise” (Center for Internet Security)
- “Stop business email compromise with three key approaches” (TechTarget)
- “14 tips to prevent business email compromise” (CSO Online)
"The Surge of BEC Attacks and How to Mitigate Damages" (RSA Conference)
"BEC: Why is nobody Talking about this Fraud?" (All Things Secured)
"How to prevent business email compromise in Microsoft 365" (IDG TechTalk)
"Don’t Let Cyber Criminals Cash In – Preventing BEC" (CISA)
6 - Check out this checklist of OT security best practices
With cyberattacks against critical infrastructure facilities on the upswing, there’s heightened awareness about protecting the operational technology (OT) systems that control industrial equipment.
This week, IANS Research published a checklist of OT security best practices based on the Purdue Reference Model for industrial control segmentation and intended as a guide, not as a comprehensive set of instructions.
Recommendations include:
- Separating IT assets from OT assets via a formal network topology
- Using network security controls, prevent Industrial Security Zone users and Cell Area Zome users from
- accessing arbitrary destinations on the internet
- accessing arbitrary destinations in the Enterprise Security Zone
- Deploy an IT/OT segmentation method, such as airgap, firewall or data diode, and ensure segmentation is secure.
- Deploy OT network modeling controls
For more information about OT security, watch these new videos from Tenable:
"The top threats to ICS systems"
"Proactively Securing ICS/OT Systems"
"ICS Security: Securing Industrial Controllers"
"Securing the Industrial Control Plane"
"Automated Asset Discovery and Management for Industrial Systems"
And one more thing! View the debut episode of Tenable Cyber Watch, a weekly video newscast that highlights topics drawn from this blog that matter for cybersecurity professionals around the world. Catch it every Monday morning on the Tenable blog or subscribe to our YouTube playlist.
- Anti-malware
- Asset Management
- Cloud
- Cybersecurity Snapshot
- DevOps
- Exposure Management
- Government
- Malware
- Metrics
- Vulnerability Management
- Vulnerability Scanning
